Key takeaways:
- A calcium score test (also called CT coronary calcium scoring) checks for calcium deposits in the heart’s arteries.
- The test helps detect early signs of plaque buildup before symptoms appear.
- It’s a quick, non-invasive scan that can estimate your risk of coronary artery disease.
- Your cardiologist may recommend it if you have risk factors like high blood pressure, diabetes, or a family history of heart disease.
- Early detection allows for lifestyle and medical steps to prevent heart problems down the line.
What is a calcium score test?
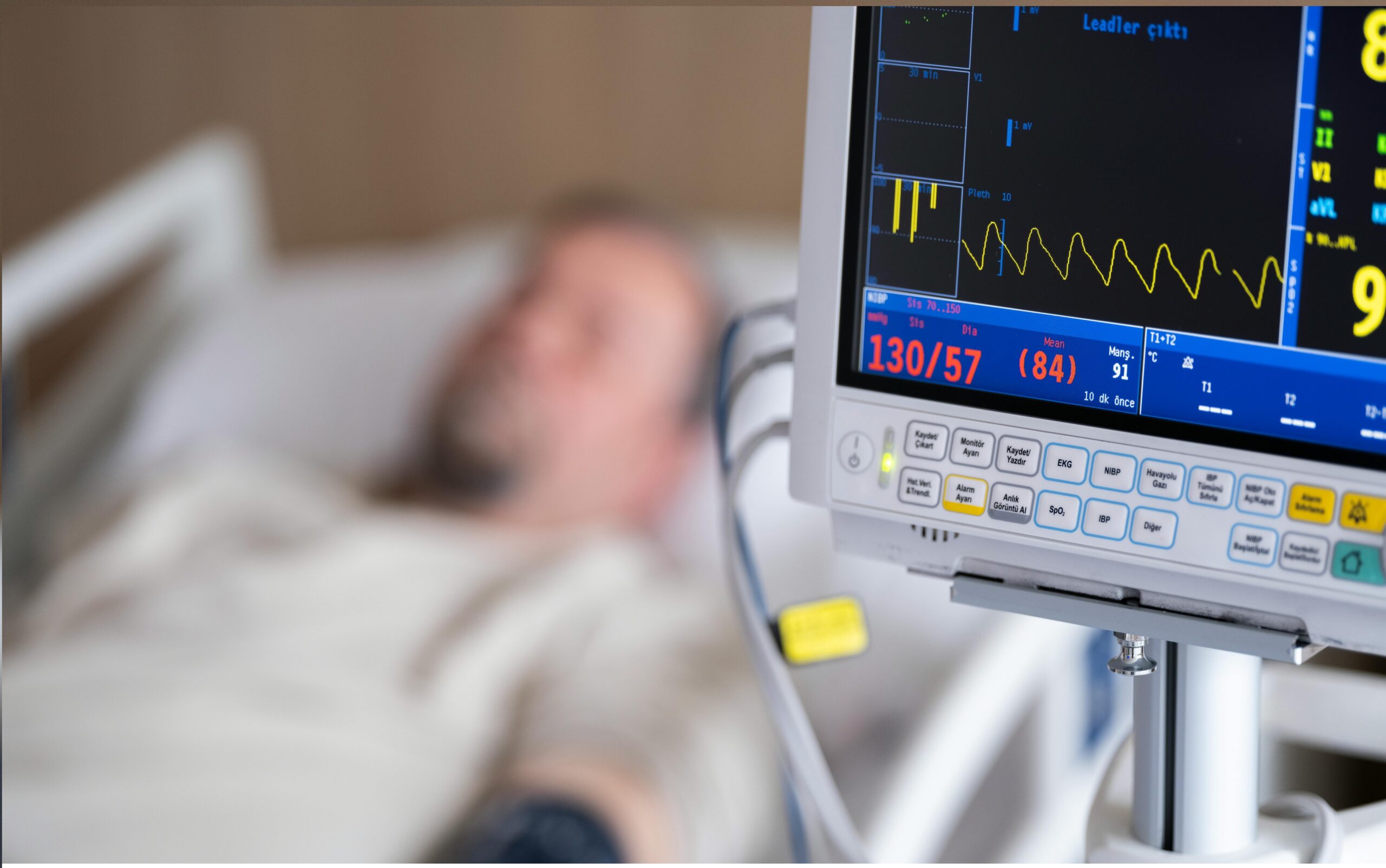
A calcium score test is a simple, low-dose CT scan that measures calcium buildup in the walls of your heart’s arteries, the coronary arteries.
When calcium is found there, it suggests that plaque (a mix of fat, cholesterol, and calcium) has started forming. Over time, this buildup can narrow the arteries, reducing blood flow and increasing the risk of heart attack or coronary artery disease.
The test produces a “calcium score,” a number that reflects how much calcified plaque is present. The higher the score, the greater the likelihood of underlying heart disease.
How does the test work?
The procedure is quick and painless. You’ll lie on a scanning table, and electrodes will be attached to your chest to monitor your heartbeat. The CT scanner takes detailed images of your heart, which are then analysed to calculate your calcium score.
No needles, dyes, or contrast agents are typically needed. The entire process usually takes less than 15 minutes.
Because it’s non-invasive, the calcium score test is a convenient way to detect early changes in the arteries before symptoms like chest pain or breathlessness appear.
What does your calcium score mean?
Your results come in the form of a number, your Agatston score. Here’s a general guide to what it means:
- Score of 0: No calcium detected. Low likelihood of coronary artery disease.
- 1–99: Mild plaque buildup. Some early signs of heart disease may be present.
- 100–399: Moderate plaque buildup. Higher chance of blockages developing.
- 400 and above: Extensive calcium buildup, suggesting a significant risk of heart problems.
It’s important to remember that a calcium score doesn’t show how severe any blockage is, but it indicates how much plaque has already formed.
Who should consider getting a calcium score test?
A calcium score test is often recommended for people with moderate risk of heart disease, those who don’t have symptoms yet but may have certain risk factors, such as:
- Family history of premature heart disease
- High cholesterol or triglycerides
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes or pre-diabetes
- Smoking
- Being overweight or physically inactive
It can also be useful if your doctor wants to fine-tune your treatment plan, such as deciding whether you may benefit from cholesterol-lowering medication or more intensive lifestyle changes.
How can early detection make a difference?
Heart disease often develops silently over many years. By the time symptoms appear, there may already be significant artery narrowing.
A calcium score test helps identify risk early, allowing for preventive action such as:
- Adopting a heart-healthy diet
- Increasing physical activity
- Managing cholesterol, blood pressure, and blood sugar
- Avoiding smoking
- Discussing preventive medications if needed
The goal isn’t just to find problems, it’s to give you and your cardiologist the information needed to prevent them.
When to discuss this test with your cardiologist
If you’re over 40, have multiple cardiovascular risk factors, or have a family history of heart disease, it may be worth talking to your cardiologist about whether a calcium score test is appropriate for you.
It’s not meant for everyone, for instance, younger adults with no risk factors may not need it. But for many, it offers an early warning sign that helps guide future care.
FAQs
1. Is the calcium score test safe? Yes. The test uses a low dose of radiation, similar to or less than what you’d receive from other common imaging tests.
2. Do I need to fast before the scan? Usually, no fasting is required. However, your clinic will let you know if any preparation is needed.
3. Does a high calcium score mean I will have a heart attack? Not necessarily. It means your risk is higher, but lifestyle changes and proper treatment can significantly reduce that risk.
4. Can the calcium score test detect soft plaque? No. It only measures hardened (calcified) plaque. Other imaging tests may be used if soft plaque is suspected.
5. How often should I repeat the calcium score test? Your cardiologist may recommend repeating it every few years, depending on your score and overall health profile.
Early insight, better prevention: why your calcium score matters
A calcium score test offers a valuable snapshot of your heart’s health, before symptoms start. Knowing your score can motivate timely lifestyle and medical decisions that help protect your heart long-term.
Wondering if a calcium score test is right for you?
If you’re managing blood pressure, cholesterol, or other heart risk factors, it may be time to check your heart’s condition more closely. Speak with a cardiologist at The Heart Practice to discuss whether a calcium score test fits into your preventive care plan.
📞 +65 6733 6811
📲 WhatsApp: +65 8926 0080
👉 Book an Appointment
📍 6 Napier Road #03-05, Gleneagles Medical Centre, Singapore